Table of Contents
What is leukoplakia?
In simple words, leukoplakia is a white patch that can occur in any part of your mouth.
The white patch is usually non-scrapable and can range from a light white area to a hard leathery white patch in the mouth.
There are various forms of leukoplakia.
Homogenous leukoplakia:
Homogenous leukoplakia appears as a white uniform patch that spreads uniformly in the region involved.
Take the first step to a better Oral health!
Get tips on Oral health and discover ways to improve your Dental health. Sign up today

Non-homogenous leukoplakia:
When you observe that the white patch is non-uniform and contains areas of red zones in between is called non-homogeneous leukoplakia.
Non-homogenous form of leukoplakia is more dangerous than a homogenous form of leukoplakia. The lesions are more aggressive than the previous.

Where do we see leukoplakia?
Leukoplakia is often seen in smokers and drinkers. It is also seen in people who chew tobacco. In short, it is a common lesion in people who have an association with tobacco.
10 things you should know about leukoplakia
Here are the 10 important points you should know about leukoplakia, before reading this post.
- Leukoplakia is a white patch that can occur in any part of your mouth.
- It is usually associated with people who take tobacco and gets aggravated in chronic drinkers.
- All forms of leukoplakia might not develop into oral cancer
- Leukoplakias that form on the floor of the mouth is more dangerous.
- The biopsy is the gold standard for leukoplakia and for confirming oral cancer transformations.
- Leukoplakia is painless
- It cannot be scrapped off like other candida lesions.
- The lesion once formed cannot be cured upon itself. You should use medication and stop the habit to contain the lesion.
- The changes that are seen in leukoplakia are irreversible. They can be only removed (by excising the tissue) but not reversed back.
- Only 3% of the lesions might transform into oral cancer.
Are leukoplakia painful?
No! leukoplakia is painless and the patient will not experience any pain in the mouth. This is the main reason why most of these lesions are unnoticed and usually get identified accidentally.
Are all leukoplakia cancerous?
No! most leukoplakias do not turn into cancer. According to a meta-analysis conducted by famous oral biologist S.Warnakulasuriya and his colleagues, the average percentage of changes for leukoplakia to convert into cancer is only 3.5%.
In his meta-analysis published in 2016, Dr.Warnakulasuriya has included 24 studies to know the average malignant transformation rate in patients having leukoplakia.
Many factors play a key role in leukoplakia turning into malignancy like smoking, drinking, genetic setup, etc.

Can leukoplakia go away?
No! leukoplakia is a permanent change that occurs in your mouth. To understand it, we should know how it forms.
The skin in the mouth contains 2 layers, the epithelium, and the connective tissue.
The epithelium is the outermost layer of the skin and connective tissue is the inner layer that contains nerves, blood vessels, and other tissues.
Let us take the example of smokers. During smoking, the high temperature of the smoke and the harmful chemicals released in smoking try to enter our skin in the mouth.
To stop this inflow of toxins, the skin in the mouth gets thickened, so that tokins might not enter the skin. This is a protective phenomenon by the body.
As a result, leukoplakia will be formed. In simple words, leukoplakia is nothing but a hardened thick tissue (you call it hyper keratinized) formed to prevent the entry of toxins into the body.
Hence the tissue once formed cannot be gone on its own. Instead, if the tissue is of small size, we can remove the tissue completely and wait for the new tissue to form.
If the tissue is large, we can apply vitamin A creams to regulate keratinization.
Can leukoplakia be scraped off?
No, leukoplakia cannot be scraped off, as the term leukoplakia indicates thickened tissue. It is a part of the epithelium and cannot be scraped off.
On the other hand, lesions from candidiasis can mimic leukoplakia as both are white. But candidiasis can be scrapped, while leukoplakia cannot be scrapped.
You will find, a red area below the scrapped tissue in candidiasis.
Can leukoplakia spread?
Yes! Even after the appearance of the lesion, if he or she continues to smoke or drink, the lesion may spread in size.
But once the risk factors are stopped, then the spread of the lesion will be decreased. In most cases it becomes stagnated and unaltered for years.
Can leukoplakia cause sore throat?
No! leukoplakia is a structural change in the mouth. It represents thickened skin in one or more areas in the mouth. Hence leukoplakia has no role to play in your sore throat.
But! When leukoplakia is turning into malignancy, it may cause some ulcers in the region and may cause a sore throat.
Hence sore throat in patients with leukoplakia in the pharyngeal region is something that should not be neglected.
A biopsy can clarify your doubts. A biopsy can reveal if there are any changes in your throat. Hence in case of any doubt consult your dentist and have a biopsy done.
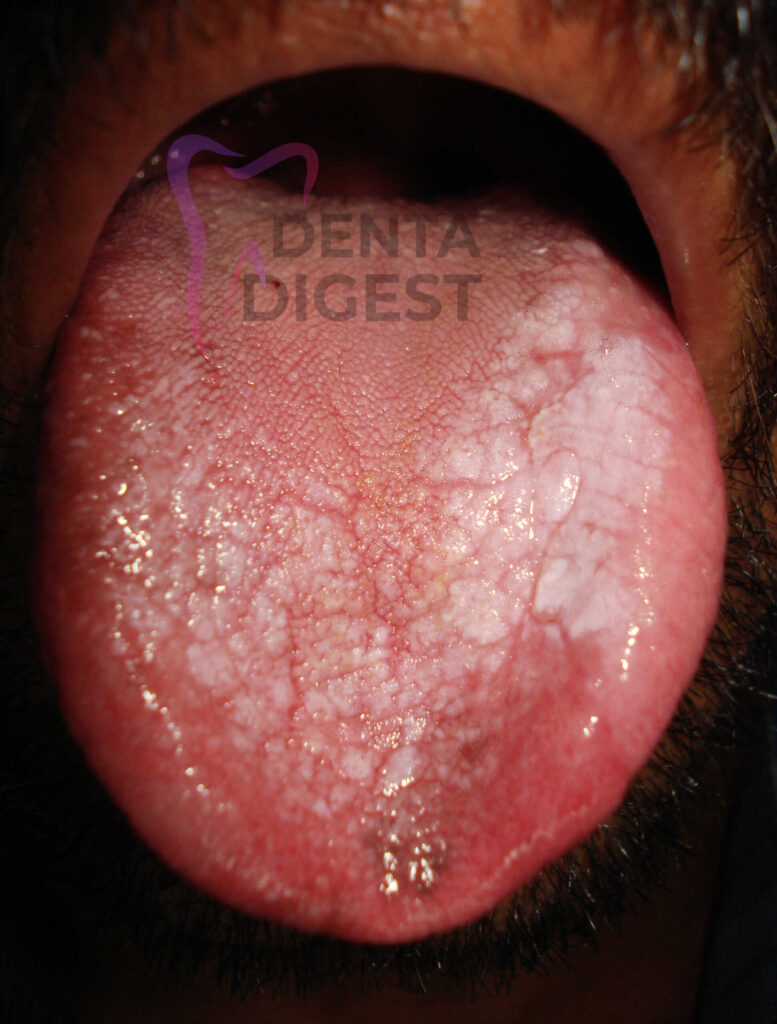
Can leukoplakia cause swollen lymph nodes?
No! leukoplakia in its natural form will not produce swollen lymph nodes. Swollen lymph nodes associated with leukoplakia in the oral cavity might indicate malignancy.
In simple words, if leukoplakia has turned into cancer, then the cells might metastasize (travel) to regional lymph nodes. In such cases, we might see swollen lymph nodes.
In case of doubt, have a biopsy to get a clear picture (Lymph node biopsy)
Can leukoplakia kill you?
No! leukoplakia can rarely turn into malignancy. Hence it might not kill a patient.
But! Leukoplakia can hamper your normal lifestyle.
How leukoplakia occurs?
Whenever toxins from smoking tobacco or chewing tobacco or alcohol try to enter the skin within our mouth, then the cells under the skin can produce more keratin over the surface.
As a result, the skin becomes thick to prevent any further toxins. This is how leukoplakia is formed.
But even after the formation of leukoplakia, I the skin is exposed to toxins, then the cells under the lesion are vulnerable to change into cancer cells. And this is how cancer develops from a pre-existing leukoplakia.
Leukoplakia on the palate is called palatal leukoplakia. Leukoplakia on the tongue is called leukoplakia on the tongue. Similarly, according to the region leukoplakia is called:
Leukoplakia on lips
Leukoplakia on the buccal mucosa
Leukoplakia on the floor of the mouth.
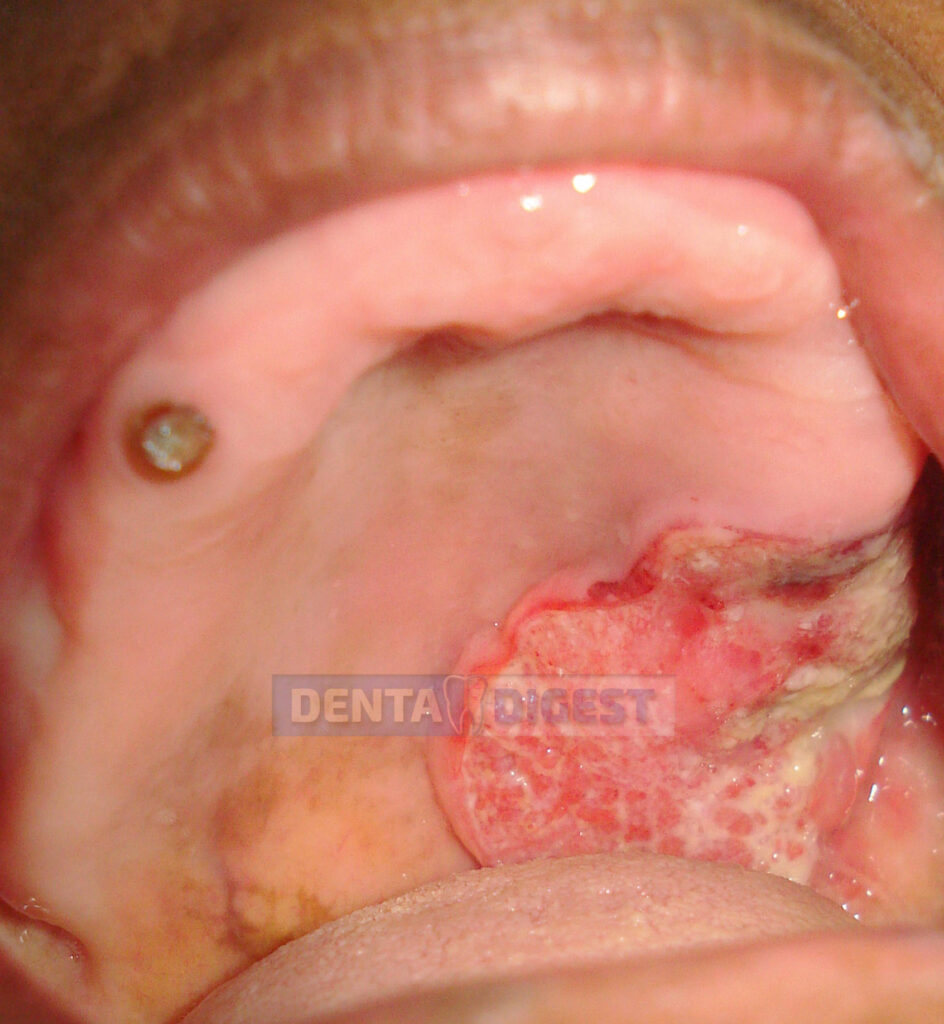
How is leukoplakia related to cancer?
Theories are suggesting that susceptible patients might develop cancer from leukoplakia.
Hence patients with leukoplakia have higher chances of turning into oral cancer.
As already mentioned, 3% of patients with leukoplakia have a chance of developing oral cancer.
Leukoplakia how long does it last?
Leukoplakia is a permanent change to your skin in the oral cavity. Hence it lasts for the rest of your life.
But if the lesion is small, and the risk factors are eliminated, there are chances that leukoplakia might disappear after some time.
But the scenario changes from person to person and a lot of other factors also play a role.
What does leukoplakia look like?
Leukoplakia is a white patch. It can be homogenous or non-homogenous.
The general presentation of leukoplakia can be compared to a dried and cracked mud presentation. But the presentation may vary from region to region.
Leukoplakia in the palatal region might range from small white dots to a large white patch.
Leukoplakia in the floor of the mouth might appear like an ebbing tide or waves that appear in the sea.
Leukoplakia on the buccal mucosa might appear like cracked mud. Leukoplakia on the lips might appear as a homogenous white patch.
How is leukoplakia diagnosed?
The best way to identify leukoplakia is with the help of a biopsy. In a biopsy, we might find excess keratin layer deposition in the skin of the mouth.
In severe cases, we might also find some cancer changes in the cells, which indicate that the lesion is converting into oral cancer.
Got diagnosed with Leukoplakia. Next what to do?
It is an important question. Once you got diagnosed with leukoplakia, you have to find whether there are any cancer changes in the cells. You can find them by having a biopsy.
If there are no cancer changes, then you can simply wait and watch. Be on antioxidants and do nothing. The lesion will not grow further when you stop all your risk factors.
On the other hand, if you find cancer changes, your dentist might opt for the excision of the lesion. He might also advise some medication.
Other than medication, there are many treatment options like cryotherapy, laser excision, and surgical excision.
Leukoplakia what to eat?
We would generally advise patients to be on diet rich in anti-oxidants like tomatoes, carrots, and leafy vegetables.
Foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids also aid in the fast healing of the lesion. Eggs are a rich source of omega-3 fatty acids.
Seafood rich in vitamin A helps in regulating keratinization. They aid in decreasing the severity of hyperkeratinization.
Foods, rich in vitamin C aid in the healing of the mucosa or the skin in the oral cavity.
What does leukoplakia look like in pictures?
The post contains a few pictures of leukoplakia in various regions of the oral cavity.
When does leukoplakia become cancer?
There is no specific time to describe the cancer changes in leukoplakia. Many factors can turn leukoplakia into cancer.
Genetic susceptibility
If your genes are more susceptible to oral cancer, then you might develop oral cancer changes very early. It is the main reason why we see oral cancer in one patient who has had a smoking habit for one year.
On the other hand, we might see another person who hasn’t developed any oral cancer in his lifetime being a chain smoker. Isn’t that interesting?
Continuation of habit
If you continue to smoke or drink even after identifying oral leukoplakia, you might have a higher chance to develop oral cancer.
The changes that occur in the body due to tobacco are permanent. In simple words, these changes are single and simple when we consider them as individual changes.
But these simple changes pile up over one another and in due course, they all combine to develop oral cancer.
Hence, this is why we see patients who develop oral cancer even after stopping tobacco for a significant period.
In simple words, let us think, a person was smoking tobacco for 10 years. Suddenly, he realized that smoking is dangerous and has left the habit. Even after leaving the habit, the person is susceptible to oral cancer as the changes that occurred previously are permanent and cannot be reversed.
Leukoplakia, when to, worry?
This is an important question. Normal leukoplakia might not turn into malignancy. There are some important changes to be noticed before leukoplakia turns into malignancy. Here are the early warning signs which might indicate cancer formation.
Redness
When you see a red component in the white areas of leukoplakia, then I would advise you to go for a biopsy for confirmation.
Redness is a sign of danger or malignant transformation.
Ulcer
If you see an ulcer developing in and around the region of leukoplakia, then you have to visit a dentist for confirmation.
Growth
If you identify any exophytic or endophytic growth or selling in the region of leukoplakia, then immediately visit a dentist and get it diagnosed. It might be developing oral cancer.
Leukoplakia when to biopsy?
All leukoplakias are not dangerous. And most of them might not need a biopsy if you stopped taking tobacco or alcohol.
But in case you or the examining dentist doubts any cancer changes, then you might get a biopsy for clarification.
The decision will be taken by the dentist if he or she might have any doubt.
When does leukoplakia appear in HIV?
In HIV patients leukoplakia will be more aggressive and might have the highest chances of malignant transformation.
It is different from hairy leukoplakia.
When does hairy leukoplakia appear?
Hairy leukoplakia is a common lesion in patients suffering from AIDS or HIV infection.
It is different from leukoplakia that you see in general. Hairy leukoplakia is a white hairy lesion seen in patients with HIV infection. It is caused by the Epstein-Barr virus (EBV).
Where does leukoplakia occur?
Leukoplakia can occur in any part of the oral cavity. It might occur on the palate called palatal leukoplakia.
It can occur on the tongue called leukoplakia on the tongue. It can occur on the floor of the mouth, the cheek region, and even on the lips and gums.
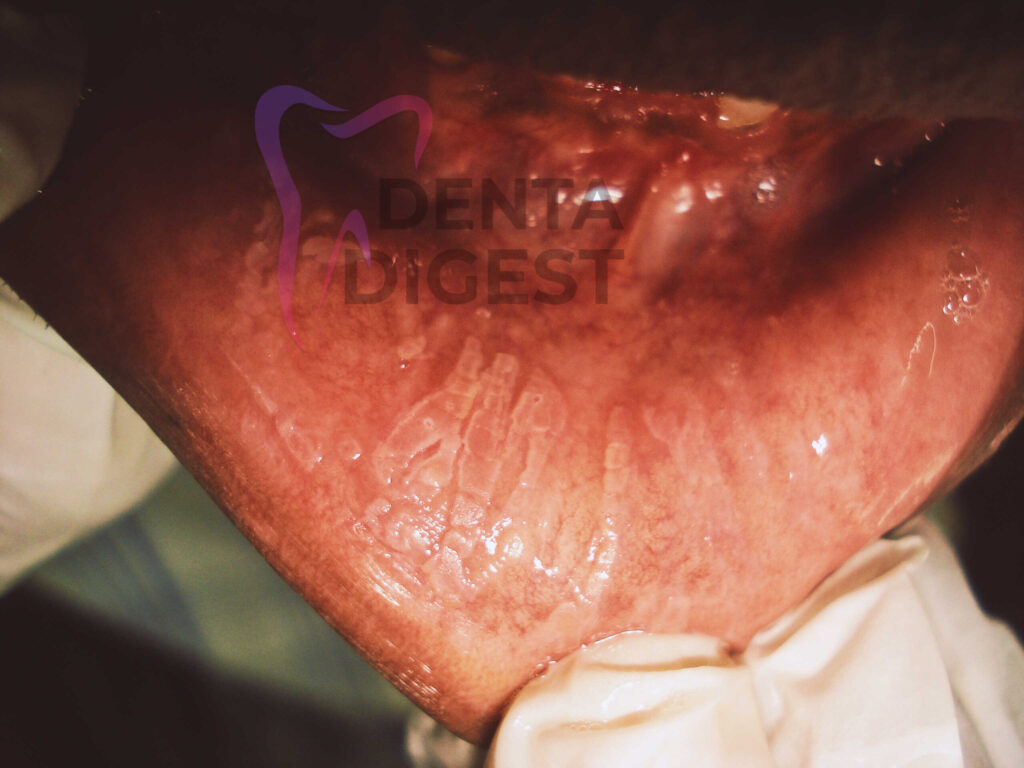
What is leukoplakia caused by?
Tobacco chewing and smoking might cause many toxins to be exposed to the skin in the mouth (mucosa).
As a result, the body forms a thick keratin layer over these areas to protect the skin from these toxins.
Leukoplakia which doctor to see?
Good question. An oral biologist or an oral medicine expert is the right person to treat such lesions.
Check for an oral medicine expert near your region and have an appointment. Or you may also ask your family dentist to register an appointment with an oral medicine expert who would be visiting his dental clinic.
Hence an oral medicine expert is a right person to treat leukoplakia.
Leukoplakia for years. Is it dangerous?
No! if you have had leukoplakia for years, and you have stopped smoking and drinking, then you might not fear any cancer changes.
The lesion that you see might be only the remnants of the disease that has formed earlier.
Leukoplakia near wisdom tooth.
Interestingly, there are many lesions in the oral cavity that might mimic leukoplakia.
For example, frictional keratosis might mimic almost leukoplakia. But the etiology is different.
Usually, the skin around the third molar might be stressed and due to repeated friction due to angulated tooth, might experience increased keratinization.
The lesion might be a frictional keratosis than leukoplakia. In case of doubt, consult your dentist and have a biopsy for confirmation.
Leukoplakia with dysplasia. What does my report indicate?
If the biopsy report says that there is leukoplakia with dysplasia, it means that the cells are changing towards malignancy or oral cancer.
Remember! It doesn’t mean that the lesion has completely changed into oral cancer. Hence there is still a chance to stop the further change of dysplasia.
Such conditions can be treated by your oral medicine expert. Consult him for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Early diagnosis and treatment will have a better prognosis.
Leukoplakia without smoking. Where do we see it?
Yes! We can see patients with leukoplakia even though they are non-smokers. People when they take any form of tobacco can get leukoplakia. For example, people who chew tobacco also get leukoplakia in the cheek region where they keep the quid (the tobacco bolus).
Frictional keratosis is similar in presentation to leukoplakia, but the reason for its occurrence is different. In simple words, as the name suggests, frictional keratosis occurs due to frictional etiology. It mostly occurs on the cheeks, gingiva, and gums.
Occasionally we may misdiagnose leukoplakia with frictional keratosis. Most patients without any habit can be misdiagnosed as having leukoplakia.
In such conditions, a biopsy can save you by providing the right diagnosis.
Leukoplakia with an ulcer. What does it indicate?
When we see leukoplakia with an ulcer, it is something that should be taken seriously.
If the ulcer is healing within a week, then it might be a normal ulcer. But if the ulcer is not healing and is constant for more than a week, then you should visit a dentist and get a biopsy done.
The ulcer might be a developing oral cancer and cannot be neglected.
Leukoplakia with pain
Leukoplakia is a painless lesion. But it might become painful until it is secondarily infected.
Leukoplakia with pain should be biopsied to rule out any oral cancer change in the skin.
Leukoplakia treatment without surgery
The regular treatment practice for leukoplakia is
- Oral antioxidants reduce free radical density in the body
- Multivitamins to increase nutritional supply
- Vitamin A creams or tablets to regulate keratinization.
** NO need for any steroids**
Lesions with cancer changes can be treated with chemotherapeutic medication like bleomycin.
Other than the conventional treatments, many research studies are indicating the usage of Aloe vera, curcumin, and green tea.
Advanced treatment modalities like photodynamic therapy have been developed to treat oral leukoplakia.
Will leukoplakia go away if you stop smoking?
No! the lesion once formed might not go unless it is mild in intensity. Usually, the changes that we see in the skin at the molecular level are permanent and might not get reversed in leukoplakia.
But once we stop smoking, there might be any further damage to the tissues.
Leukoplakia and lichen planus. What’s the difference?
Leukoplakia and lichen planus are completely different. They are not inter-related.
Leukoplakia occurs due to smoking and drinking and is a thick keratinized area on the mucosa (skin inside the mouth).
On the other hand, oral lichen planus (OLP) is an inflammatory condition where the cells inside the junctional epithelium (cellular level of the skin) get damaged.
Leukoplakia is a regular lesion developed due to habits. But, OLP has an autoimmune etiology and cannot be related to leukoplakia.
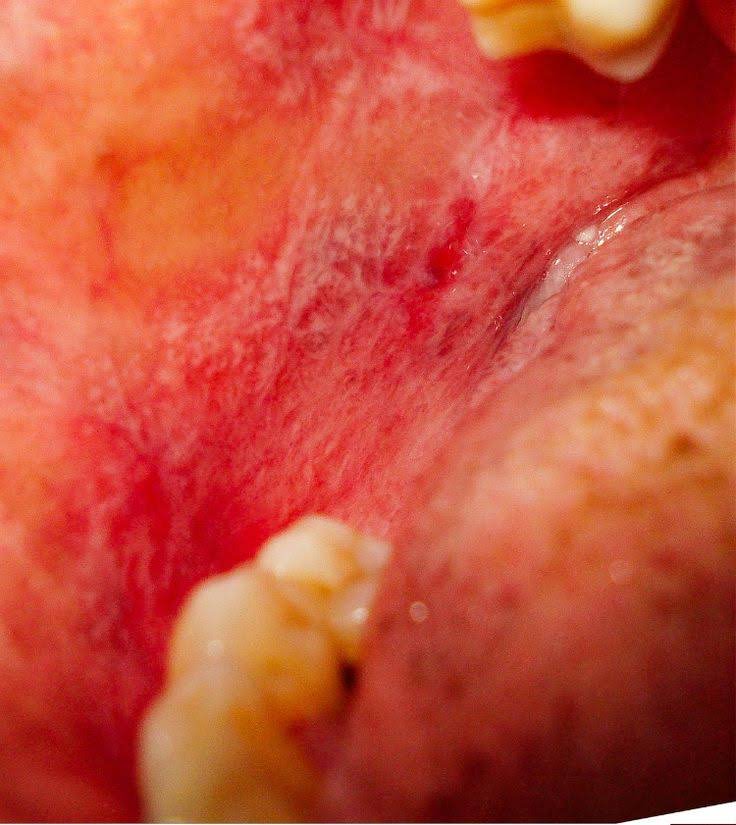
Often plaque form of OLP mimics leukoplakia if it occurs on the tongue. A biopsy is a gold standard to differentiate leukoplakia from OLP.
- Is oral hygiene compulsory for kids? - January 13, 2023
- How to Choose the Best Dental Crown for Your Smile? - December 8, 2022
- Who needs antibiotics before dental work? What is antibiotic prophylaxis? - October 31, 2022




Pingback: ORAL LICHEN PLANUS. HOW SHOULD I MANAGE? | DENTA DIGEST
Pingback: 16 things no one tells you about tooth extraction | DENTA DIGEST