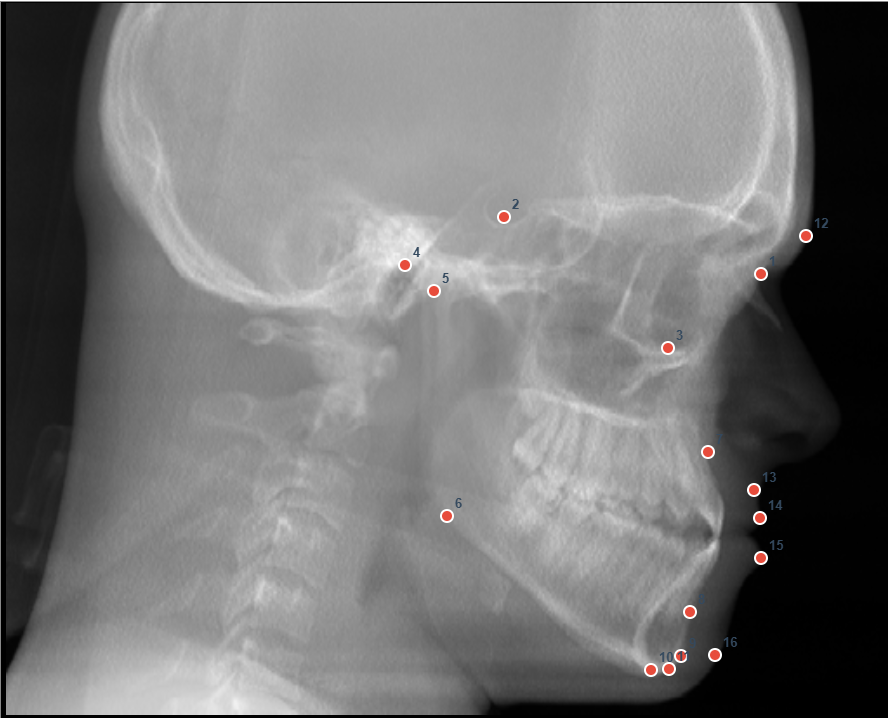
Upload a lateral cephalogram and mark each landmark in order. Results will be shown in a table after all landmarks are marked.
Table of Contents
Landmarks to Mark (in order):
- Sella (S)
- Nasion (N)
- Point A (A)
- Point B (B)
- Gonion (Go)
- Gnathion (Gn)
- Pogonion (Pg)
- Menton (Me)
- Upper Incisor Tip (U1 Tip)
- Upper Incisor Apex (U1 Apex)
- Lower Incisor Tip (L1 Tip)
- Lower Incisor Apex (L1 Apex)
- Soft Tissue Pogonion (Pog’)
- Columella (midpoint of lower border of nose)
What is Steiner’s Analysis?
Steiner’s cephalometric analysis is a foundational orthodontic diagnostic method developed by Dr. Cecil C. Steiner in 1953. It uses specific anatomical landmarks on a lateral skull X-ray (teleradiograph) to construct reference lines and angles. By comparing a patient’s measurements to established norms, clinicians can identify skeletal and dental discrepancies and plan individualized orthodontic or surgical treatments.
Why is Steiner’s Analysis Important?
Steiner’s analysis is widely used because it provides a clear framework to:
- Assess the anteroposterior positions of the maxilla and mandible (SNA, SNB, ANB angles)
- Evaluate the inclination and position of the upper and lower incisors
- Analyze facial proportions and soft tissue harmony (using the S-line)
- Classify malocclusions (Class I, II, III) and determine the origin (skeletal, dental, or both) of the problem135
This comprehensive approach ensures that treatment is tailored to the patient’s unique skeletal and dental relationships.
What Does Steiner’s Analysis Measure?
Steiner’s analysis is divided into three main components:
Take the first step to a better Oral health!
Get tips on Oral health and discover ways to improve your Dental health. Sign up today
- Skeletal Analysis:
- SNA (maxilla to cranial base)
- SNB (mandible to cranial base)
- ANB (maxilla to mandible)
- Mandibular and occlusal plane angles
- Dental Analysis:
- Upper incisor to NA (angle and distance)
- Lower incisor to NB (angle and distance)
- Interincisal angle (upper to lower incisor)
- Lower incisor to chin (Holdaway ratio)
- Soft Tissue Analysis:
- S-line (relationship of lips to the line from the tip of the nose to soft tissue pogonion)
By analyzing these values, orthodontists can diagnose whether a malocclusion is due to jaw position, tooth inclination, or a combination, and select the most effective treatment approach1357.
Introducing the Steiner’s Analysis Tool
To bring the power of Steiner’s analysis to your fingertips, I have developed an interactive Steiner’s Analysis Tool for orthodontists, students, and researchers.
Key Features:
- Upload a lateral cephalogram (side-view skull X-ray)
- Mark all required anatomical landmarks directly on the image
- Automatic calculation of all essential Steiner measurements (SNA, SNB, ANB, incisor positions, S-line, and more)
- Results table showing measured values, normal values, and clear clinical interpretations and suggestions
How Does It Work?
- Upload your patient’s lateral cephalogram.
- Mark each landmark as prompted by the tool.
- The tool calculates all major Steiner parameters instantly.
- Results are displayed in a user-friendly table-including your measured value, the normal value, and a concise interpretation with treatment suggestions.
Why Use This Tool?
- Saves time: No manual tracing or calculations required.
- Educational: Perfect for learning and teaching cephalometric analysis.
- Accurate and reliable: Based on established Steiner norms and clinical guidelines.
- Immediate feedback: Get actionable insights for diagnosis and treatment planning.
Conclusion
Steiner’s analysis remains a gold standard for orthodontic diagnosis and treatment planning. With the interactive Steiner’s Analysis Tool, you can quickly perform comprehensive cephalometric assessments-helping you deliver precise, individualized care for every patient.
- Steiner’s Cephalometric Analysis – Free cephalometric analysis - June 7, 2025
- COGS CEPHALOMETRIC ANALYSIS – FREE TO USE - June 7, 2025
- Can You Eat on Root Canal Treated Teeth? Everything You Need to Know - May 18, 2025


